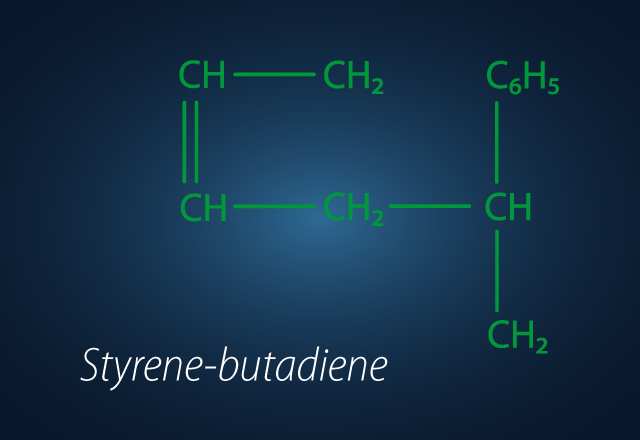
SBR
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is a synthetic elastomer used as a cost-effective alternative to natural rubber. The addition of styrene not only reduces production costs but also improves wear resistance and adhesion properties. Moreover, styrene enhances the strength, abrasion resistance, and blending properties of polybutadiene.
Although SBR has weaker fatigue resistance and lower performance at low temperatures compared to natural rubber, it offers superior heat aging resistance and wear resistance. Due to the double bonds in its polydiene backbone, SBR is, like natural rubber, sensitive to thermal and oxidative degradation. This degradation often leads to cross-linking, resulting in increased hardness (brittleness). Additionally, SBR has poor chemical resistance, making it less resistant to solvents and weathering compared to other elastomers.
Applications
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) can be used in applications similar to those of natural rubber elastomers but is less suitable for high dynamic applications due to its lower fatigue resistance. Typical applications of SBR include drive couplings, traction pads, conveyor belts, shoe soles and heels, adhesives, roller coverings, and automobile tires. Approximately 50% of car tires are made from various types of SBR. In addition, SBR is widely used in many molded rubber products.
HARDNESS RANGE:
30 to 95 Shore A

- Styrene-butadiene
- Injection
- Compression
- Extrusion
- Sulfur
- Other
- Optional