NBR
Nitrile rubber (NBR) possesses physical and chemical properties that make it one of the most widely used synthetic elastomers globally. Compared to natural rubber, NBR offers greater resistance to oils and acids and higher strength but has lower flexibility. As the nitrile content in the polymer increases, its oil resistance improves, but its elasticity decreases. Additionally, NBR’s ability to withstand a wide temperature range of −40°C to 108°C makes it an ideal compound, especially for the aerospace industry.
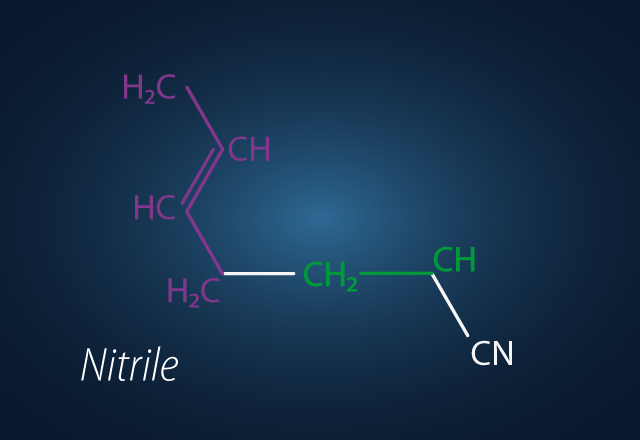
Nitrile rubber is synthesized through a chemical reaction that combines butadiene and acrylonitrile into a single compound. The resulting rubber is not only resistant to oils but also provides excellent tear and abrasion resistance. NBR compounds offer protection against petroleum oils and a variety of chemicals such as ammonia, methyl alcohol, copper salts, detergents, mercury, potassium salts, and zinc sulfate. These corrosive substances are particularly hazardous for non-nitrile materials.
Applications
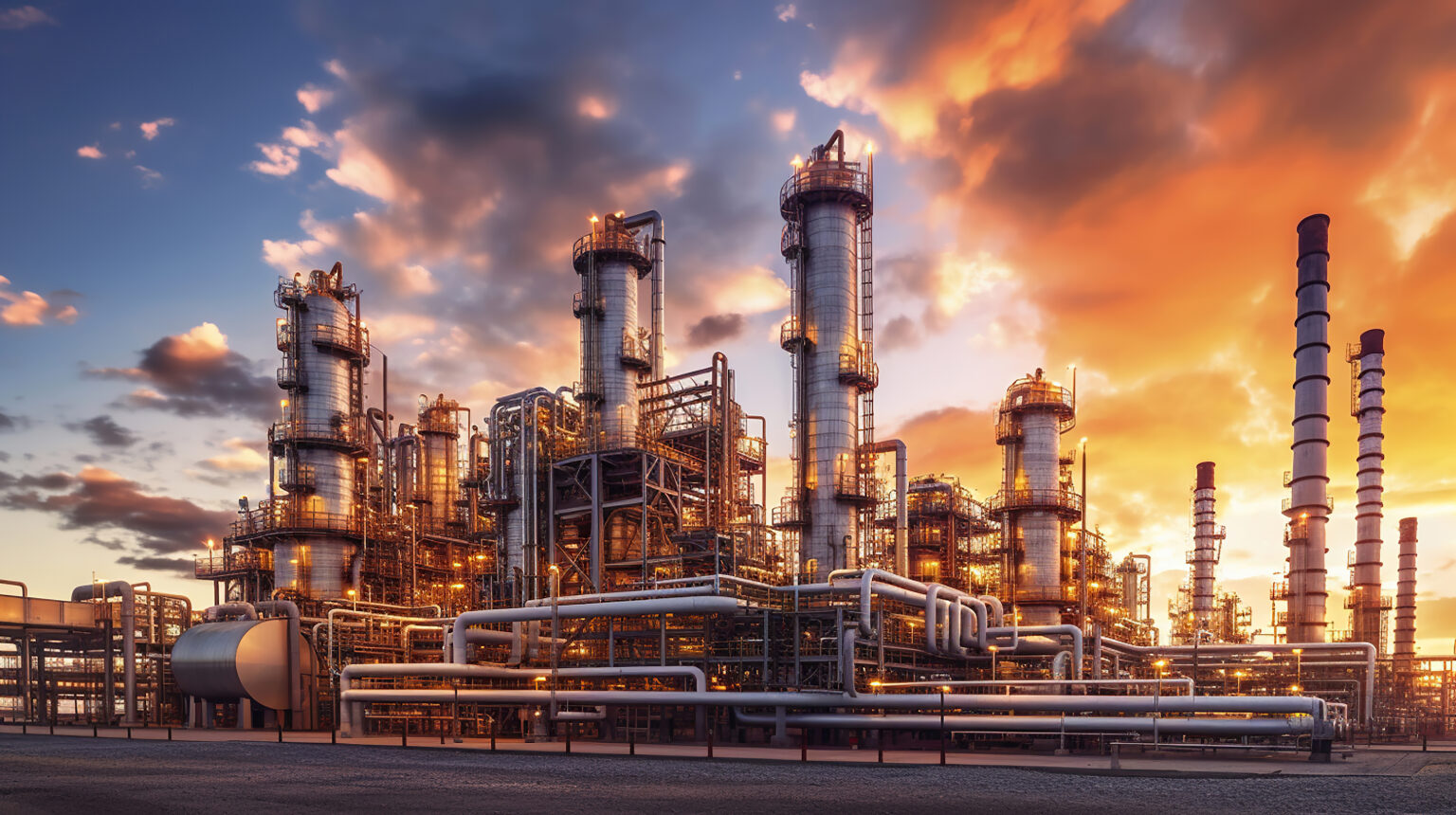
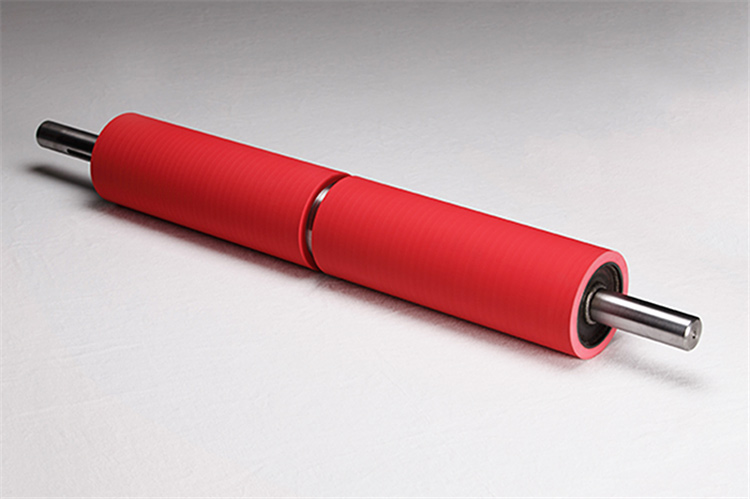
NBR is widely used in industries such as petroleum and gas production, food processing, automotive, and aerospace. These sectors require fuel and oil hoses, gaskets, seals, blind plugs, and self-sealing fuel tanks that can withstand the abrasive effects of various oils, greases, and chemicals. NBR compounds are also utilized in laboratory environments and for cleaning and examination gloves exposed to corrosive substances. Additionally, molded NBR products are used to manufacture shoes, adhesives, sealing materials, sponges, expanded foams, and floor mats.
HARDNESS RANGE:
18 to 95 Shore A

- Nitrile
- Injection
- Compression
- Extrusion
- Sulfur
- Peroxide
- Optional